
Risk Maturity Assessment
Develop your organization using RMA – Risk Maturity Assessment.
Get in touchRISK MATURITY ASSESSMENT
THE FUNDAMENTAL PILLAR FOR THE FUTURE OF ORGANIZATIONS
In today's dynamic global scenario, risk management maturity emerges as a critical component for the success and sustainability of organizations.
According to the AICPA's 2023 State of Risk Oversight research, many organizations still do not adopt effective risk monitoring and communication practices.
Only 29% of organizations describe their risk management processes as "mature."
The integration between risk management and strategic decisions is often overlooked, despite its critical importance.

In addition to the challenges and opportunities identified in the 2023 State of Risk Oversight research, risk management maturity is influenced by various critical factors, as highlighted below.
- Leadership and commitment of top management;
- Integration of risk management into business processes;
- Continuous learning and improvement;
- Effective communication and transparency;
- Adoption of process-based approaches;
- Challenges and strategies to overcome obstacles.
Organizations need to not only recognize the importance of risk management but also implement robust and strategic practices to ensure resilience and seize opportunities in a constantly changing world.
RMA – RISK MATURITY ASSESSMENT
The Risk Maturity Assessment Module of the t-Risk Platform represents an innovative and comprehensive tool designed to elevate organizations' maturity in risk management.
RMA is structured into 11 essential dimensions, 39 practices (actions correlated to maturity levels), all aligned with best practices and international standards, such as ISO 31000.
Now, on the next page, let's explore how each dimension contributes to efficient and effective risk management.
SUMMARY OF THE 11 DIMENSIONS
STRATEGY AND RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY
Assesses the existence of an informal strategy and risk management policy to the definition of a documented and implemented risk appetite.
STRUCTURE AND RESPONSIBILITY
Includes the presence of a risk management department, clearly defined roles, and an integrated governance structure.
TOP MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT
Evaluates leadership support, ranging from passive support to the active presence of a director in the risk management committee.
COMMUNICATION AND TECHNOLOGY
Analyzes personnel qualifications to the use of integrated software for risk management.
CONTEXT, ASSETS, AND PROCESSES
Evaluates asset classification and the identification of the organizational context, both internal and external.
IDENTIFICATION AND ESTIMATION OF RISK CAUSES
From exhaustive analysis of external and internal causes to proactive identification of potential risk sources.
QUANTIFICATION AND MEASUREMENT OF RISKS
Analyzes the understanding of risks, from probability and impact analysis to cumulative effects analysis.
RISK ASSESSMENT
Assesses the significance of risks and compares them with pre-established criteria.
RESPONSE TO RISKS
From defining basic responses to resilience and business continuity strategies.
MEASUREMENT OF RESPONSES TO RISKS
Analyzes the effectiveness of responses through key indicators and residual risk assessment.
IMPROVEMENT OF RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
From information gathering for learning to the implementation of continuous improvements.
STRATEGY AND RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY
Assesses the existence of an informal strategy and risk management policy to the definition of a documented and implemented risk appetite.
STRUCTURE AND RESPONSIBILITY
Includes the presence of a risk management department, clearly defined roles, and an integrated governance structure.
TOP MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT
Evaluates leadership support, ranging from passive support to the active presence of a director in the risk management committee.
COMMUNICATION AND TECHNOLOGY
Analyzes personnel qualifications to the use of integrated software for risk management.
CONTEXT, ASSETS, AND PROCESSES
Evaluates asset classification and the identification of the organizational context, both internal and external.
IDENTIFICATION AND ESTIMATION OF RISK CAUSES
From exhaustive analysis of external and internal causes to proactive identification of potential risk sources.
QUANTIFICATION AND MEASUREMENT OF RISKS
Analyzes the understanding of risks, from probability and impact analysis to cumulative effects analysis.
RISK ASSESSMENT
Assesses the significance of risks and compares them with pre-established criteria.
RESPONSE TO RISKS
From defining basic responses to resilience and business continuity strategies.
MEASUREMENT OF RESPONSES TO RISKS
Analyzes the effectiveness of responses through key indicators and residual risk assessment.
IMPROVEMENT OF RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
From information gathering for learning to the implementation of continuous improvements.
STRATEGY AND RISK MANAGEMENT POLICY
Assesses the existence of an informal strategy and risk management policy to the definition of a documented and implemented risk appetite.
STRUCTURE AND RESPONSIBILITY
Includes the presence of a risk management department, clearly defined roles, and an integrated governance structure.
TOP MANAGEMENT COMMITMENT
Evaluates leadership support, ranging from passive support to the active presence of a director in the risk management committee.
COMMUNICATION AND TECHNOLOGY
Analyzes personnel qualifications to the use of integrated software for risk management.
CONTEXT, ASSETS, AND PROCESSES
Evaluates asset classification and the identification of the organizational context, both internal and external.
IDENTIFICATION AND ESTIMATION OF RISK CAUSES
From exhaustive analysis of external and internal causes to proactive identification of potential risk sources.
QUANTIFICATION AND MEASUREMENT OF RISKS
Analyzes the understanding of risks, from probability and impact analysis to cumulative effects analysis.
RISK ASSESSMENT
Assesses the significance of risks and compares them with pre-established criteria.
RESPONSE TO RISKS
From defining basic responses to resilience and business continuity strategies.
MEASUREMENT OF RESPONSES TO RISKS
Analyzes the effectiveness of responses through key indicators and residual risk assessment.
IMPROVEMENT OF RISK MANAGEMENT PROCESS
From information gathering for learning to the implementation of continuous improvements.
AND 39 PRACTICES OF RMA
RESULTS AND ACTION PLAN
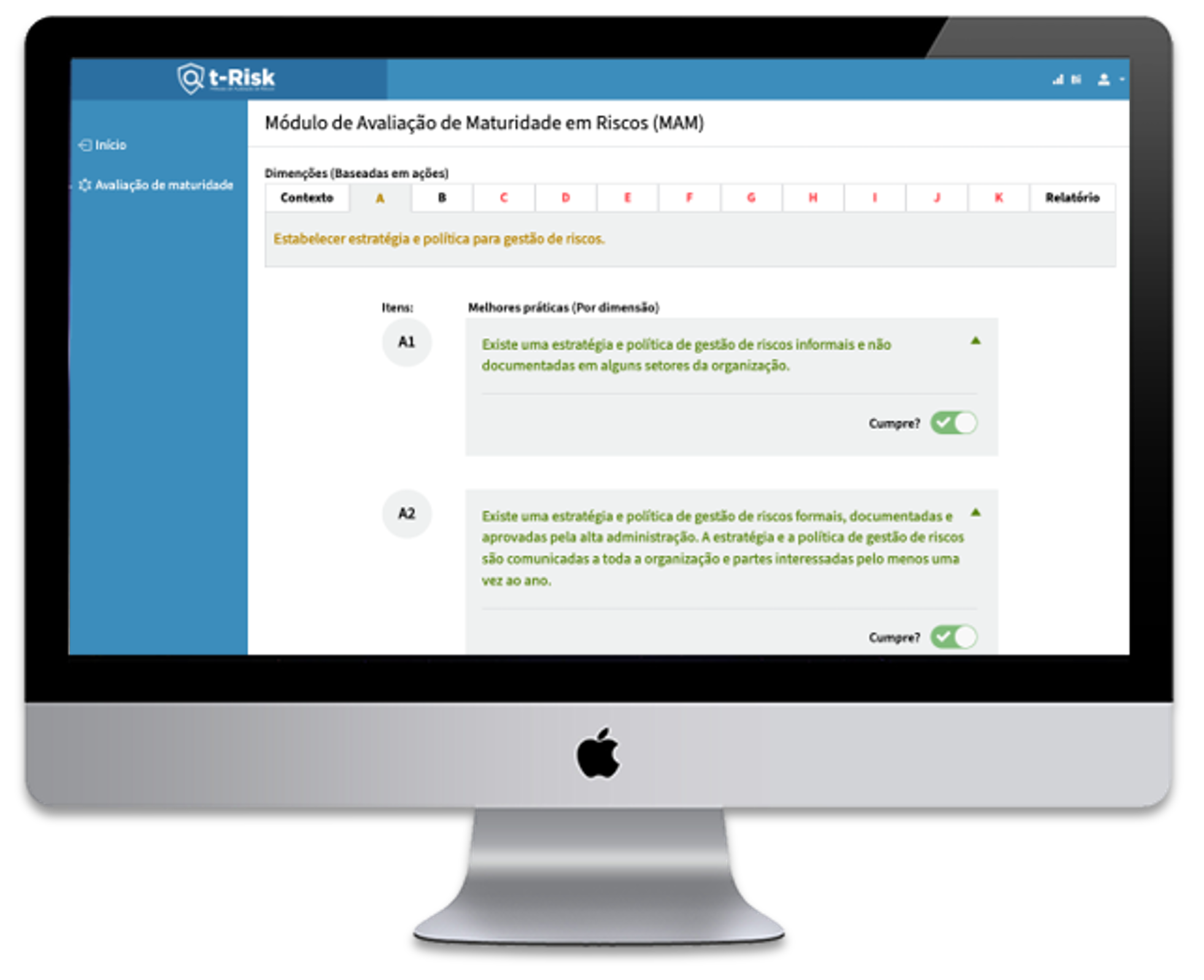
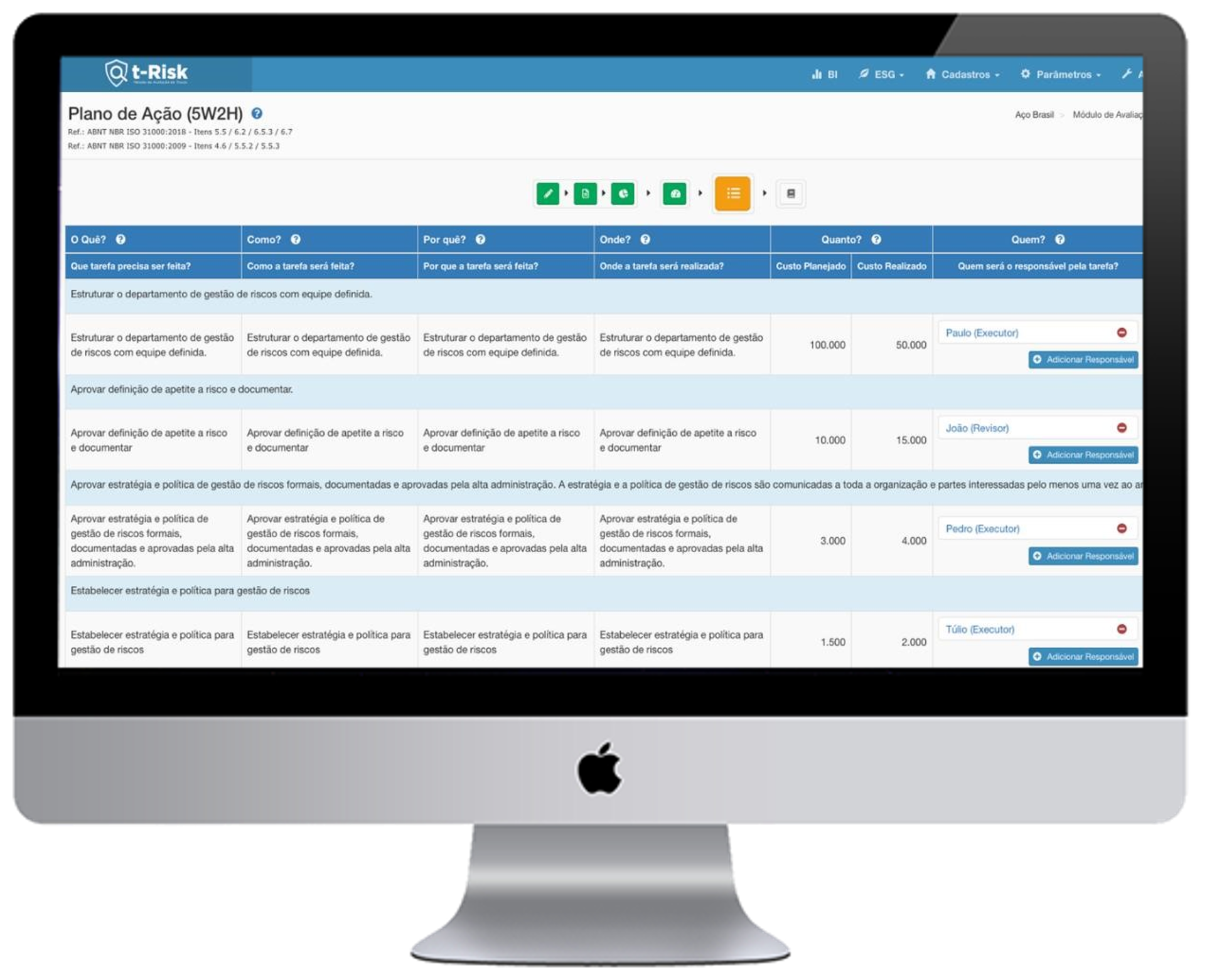
After the assessment, RMA provides a detailed diagnosis of the maturity level in each of the 11 dimensions and also in a consolidated form. This objective analysis facilitates the identification of practices that need development.

RMA MODULE DIFFERENTIATORS

One of the most innovative and valuable aspects of the t-Risk Platform's Maturity Assessment Module is its ability to analyze an organization's maturity level in each of the 11 critical dimensions of risk management.

This detailed analysis allows a deep and differentiated understanding of risk maturity, going far beyond a general assessment.

RMA distinguishes itself with its multifaceted approach, assessing each risk dimension on a five-stage scale.
RISK MATURITY
RISK MANAGEMENT MATURITY LEVELS
Immature
Level 1
Indicates an initial phase where risk management practices are nonexistent or inconsistent.
Initial
Level 2
Represents the beginning of recognition and implementation of risk management practices, though still at a basic stage.
Managed
Level 3
Denotes a stage where risk management practices are formalized and systematically managed.
Mature
Level 4
Reflects advanced and effective integration of risk management into the organization's operations and strategies.
Advanced
Level 5
Means that risk management is conducted at a strategic level, with innovative practices and leadership in its segment.
BENEFITS OF DETAILED ANALYSIS

Focused development RMA allows organizations to identify which dimensions need more attention and development, enabling efficient allocation of resources to critical areas.

Recognition of strengths At the same time, the tool highlights areas where the organization is already advanced, allowing these strengths to be maintained and enhanced.

Balanced development With detailed analysis by dimension, organizations can advance in a balanced manner, ensuring that all aspects of risk management are aligned and contribute to the overall maturity of the company.

Resource savings By avoiding overlapping efforts in already well-developed areas, the organization can save significant resources, directing them to dimensions that truly need improvement.
EFFECTIVENESS AND STRATEGY
This detailed and personalized approach of RMA not only enhances the effectiveness of risk management but also provides a clear path for continuous and balanced improvement in all facets of risk management.
With t-Risk's RMA, organizations gain not just an assessment tool but a strategic partner in the development of risk maturity.
BENEFITS OF DETAILED ANALYSIS

The Risk Maturity Assessment Module (RMA) of the t-Risk Platform provides organizations with a clear assessment of their current maturity in risk management and a practical roadmap for continuous improvement. By adopting RMA, organizations can strengthen their resilience, make more informed decisions, and strategically position themselves for long-term success.

Explore RMA and take a significant step toward more mature and effective risk management. After all, in a world full of uncertainties, the ability to manage risks efficiently is not just a competitive advantage—it is a strategic necessity. Contact us through our website and request a demonstration.